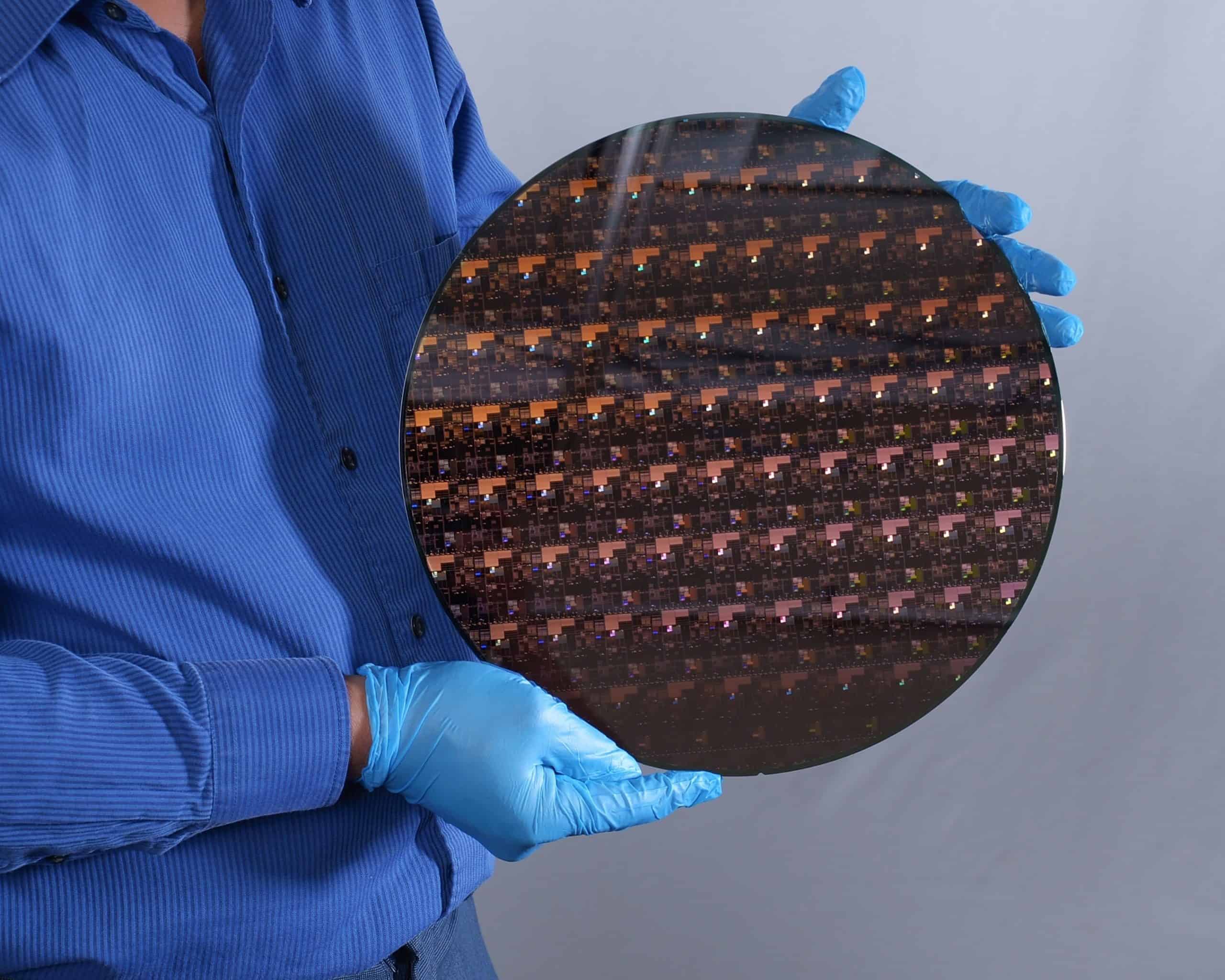
IBM’s new 2nm chip consumes 75% less power than 7nm ones.

On May 6, 2021, IBM announced on its blog that it had created the first 2nm microprocessor. Compared to those of 7nm, for the same performance, Big Blue’s new chip consumes 75% less energy. Using as much power as for the 7nm chips, the 2nm microprocessor has a performance increased by 45%. The autonomy of the new IBM chip would be up to 4 times greater than that of 7nm processors.
Another technological feat advanced by IBM: 50 billion transistors – a type of semiconductor used in most electronic circuits – have been integrated on a chip the size of a fingernail. An abstract measure clarified by AnandTech who contacted the company. According to IBM, a fingernail would be 150 square millimeters. Therefore, the 2nm chip comprises 333 million transistors per square millimeter (MTr/mm2).
In comparison, the chip M1 of Apple and Kirin 9000 Huawei, both outputs to independent 2020 are engraved in 5nm from technology owned by Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC). TSMC is also working on 2nm chips and will start producing 3 and 4nm chips next year.
Concretely, this advance would make it possible to reduce the number of charges of electronic devices by increasing their autonomy. Computers would speed up and autonomous vehicles would reduce the time to detect and react to objects. For IBM, the new microprocessor will benefit data center energy efficiency, space exploration, artificial intelligence, 5G, 6G and quantum computing. IBM has announced no release date. This year, Big Blue will sell its first 7nm chips present in Power Systems servers.
