We gathered feedback from over 100 marketers on how they use the Google Search Console to improve their SEO. This article contains a summary of expert opinions and some detailed instructions.
There are many SEO tools. According to G2, there are over 200, and most come at a cost. Each tool has its own set of data and its settings. It is therefore complicated to know which one to choose.
One of the best tracking tools is therefore the Google Search Console. It can help you with a lot of things and it’s free.
Even if you think you know this tool, it is always interesting to learn from the experiences of your peers. We surveyed over 100 marketers and gathered their tips to create this guide. It will help you get the most out of Search Console for your SEO.
As a first step, you need to educate yourself about essential data and how to find it. Then, immerse yourself in the opinions of the experts who will advise you on the best ways to use the Google Search Console to gain traffic and rankings.
Know what your essential SEO metrics are.
Remember, you shouldn’t focus on just one metric, as it could be misleading.
The most analyzed metric is that of clicks:
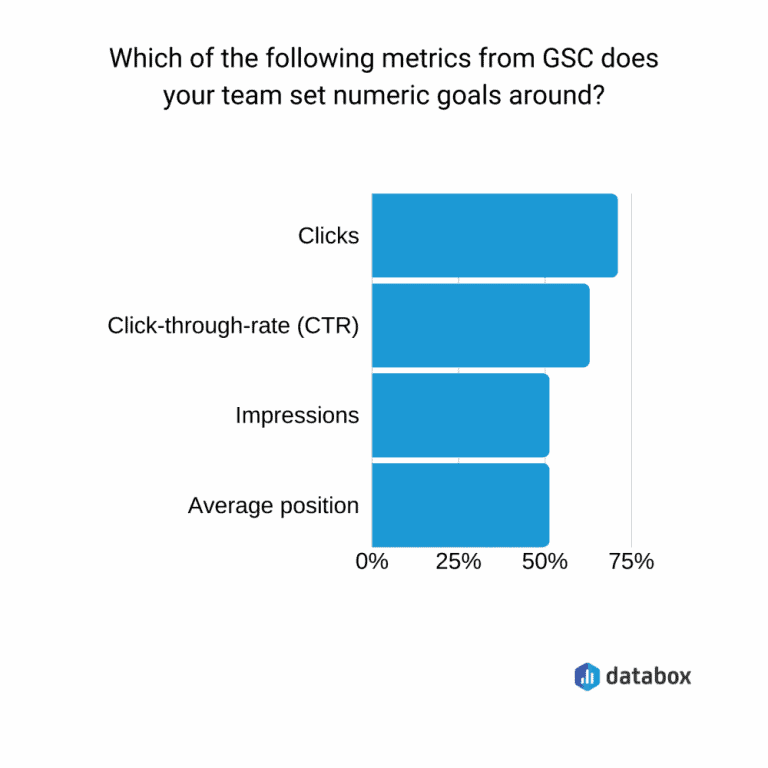
However, it is advisable to analyze impressions, CTR, and average positions. In this situation, clicks are irrelevant as they are simply the result of KPIs of CTR and impressions.
A high number of impressions and an outstanding average position can occur if you score well for certain keywords, but do not match the search intent. This information can give you the false impression that your results are excellent.
Avoid falling into the data trap.
The simplest things are often the best.
The Google Search Console has many settings, and it’s easy to fall into the data trap.
There are a few prominent terms and steps you need to follow. Know your top five search terms, which ones are most relevant to your brand, and which are most likely to generate leads.
Check your data regularly and know how to follow up in general. Additionally, you need to monitor your essential clicks and impressions metrics and observe the long term trendline.
Daily fluctuations are normal, but monthly changes are more crucial. Pay attention to the big picture as much as to the details. There can be too much data in Google’s console, and it’s easy for anyone to get lost in nuanced decision making.
Think about how you approach your content strategy and how your data informs it. If you are overwhelmed by the amount of data you have, reduce the noise and direct it to the most critical measurements.

Take your data out of the tool.
Export data from GSC for analysis in other tools like Excel or Google Data Studio.
It is simple to export the tool’s data into a document that can break it down by specific pages, countries, queries, and devices.
This operation ensures that the data is saved. This method allows you to perform more sophisticated analyzes.
Use Google Data Studio to mix data so you can cross-match positions with Analytics data and get a much deeper view of performance.
With this strategy, you can quickly see trends in performance. For example, you will see a% change in CTR or position over some time.
Track the performance of local keywords.
You can add a URL query to the main website field in Google My Business. Then use GSC to see what keywords people are using to find and click on local results.
Use the “Exact URL” page filter in GSC to differentiate a page’s standard organic clicks from its local organic clicks. This method provides granular search term information that can be used to increase local SEO efforts.
SERPs are hyper-localized, and there is massive variation in rankings and traffic down to city and town data.
Keywords that you think rank well for the whole country can be ranked poorly locally if local competitors target the same keywords. You have to pay attention to the geographic filters of the tool.
It is better to integrate GSC into Google Analytics. This method can help refine the data affected by location in a much more granular way.
Study the countries tab.
Another tip for using GSC to track SERPs is to keep an eye on the “Country” tab.
Monitor the countries of your SERPs, so you can adjust your future SEO strategies to target the countries you want.

Look at mobile vs desktop traffic.
Review the devices in the GSC Performance Report. Many forget that the majority of their traffic probably comes from mobile devices and that mobile rankings may differ from desktop ones.
Check out the devices section to see which devices are getting the most traffic.
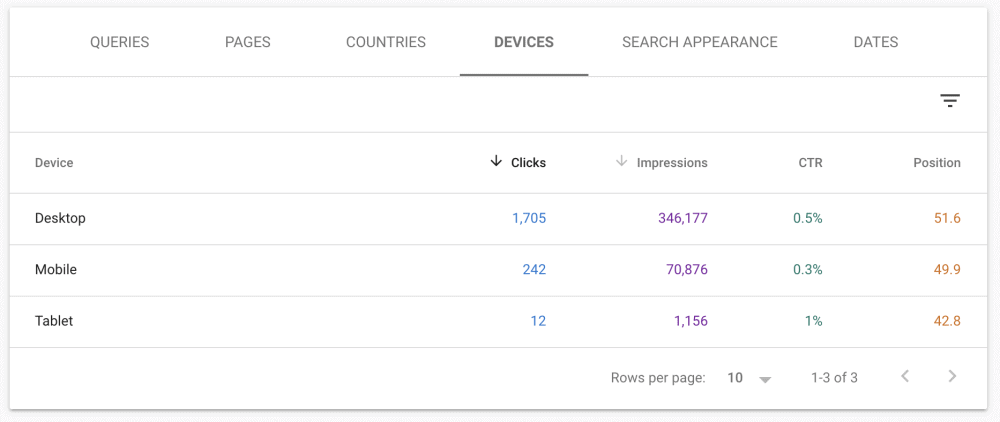
You can come up with some great reports that will help you show how effective your SEO is. You will see a gradual increase in mobile traffic if you have great SEO.
Examine the parts of your website in detail.
A great way to start tracking your rank is to open the performance report, view it by pages (URLs), then click on the filter button and use the include / exclude feature to monitor the different sections of the ranking. site, including /blog/ or /services/.
Then you can zoom in and watch CTRs, clicks, and more on different devices and in different regions.
It can be essential to have information on multiple pages when it comes to reporting.
A great tip for using the tool is to focus on user queries in your blogs carefully. These queries help you master the intent of the keywords that allow you to refine your blog and rank it better.
When your page hits the top 10, try to focus more on the CTR by manipulating the title and meta.
Mitigate keyword cannibalization.
Marketers recommend that you identify possible keyword cannibalization issues using the “Query” filter. You should show the pages that rank for that term and filter to compare the top 2 pages by impressions using “Compare”.
With the “Impressions” or “Average Position” tab, you will find out where the pages ended up in the search results for the target term.
This method is inconclusive in identifying cannibalization issues, but it will allow you to spot instances where one page that starts to rank drops another.
Compare keyword predictions with real-time rankings.
Reevaluate your keyword ranking goals regularly, every few months, by comparing those you track daily in Ahrefs with those listed in the GSC report.
This will show you which keywords you have unintentionally won. You will be able to focus on optimization efforts for those themes and spend less energy on the issues that concern you.
You should always watch your keywords. If they don’t rank then you need to rotate and pick new keywords and make sure your original keywords are SEO-friendly.
Check if there are site coverage issues
The Cover tab is a feature that brings significant added value. It allows you to identify and track errors that could impact the entire site, search rankings, or specific pages. It allows you to define things, including server errors, unindexed pages, crawl problems, URLs not found, etc. The tool allows you to fix issues, reindex, and notify Google that the issues are resolved.
On the Performance tab, monitor the number of clicks and impressions of each page that you fixed as well as the gains after optimization.

The index status allows you to check which URLs are indexed, blocked, or deleted by Google. You can also find out why, correct errors, and make improvements that generate better results.
Use the Google Search Console to find website errors, security, or indexing issues affecting your rankings.
Submit new URLs for the inspection tool.
Google may take a few days to find your URL. During this time, you refresh your data to verify the immediate impact. However, there isn’t one because Google doesn’t yet know your content exists.
After posting a new post or improving an old one, you must resubmit its URL through the URL Inspection Tool.
If you don’t, Google may not notice the changes immediately. Get your URL reindexed ASAP.

By doing this, you encourage the crawler to crawl and index your content faster, so that you can get organic traffic ASAP.
Here are two steps you can take.
- Paste the post/page URL in the search bar and wait for the page to process your link. Make sure it does not have any additional parameters.
- Click on “Indexation request”. If there is a problem, correct the errors first before submitting the link.
You can use Yoast SEO to generate a sitemap that you will submit to GSC. Sitemaps make it easy to crawl and index.
Inspect the canonical parameters of the domain.
Be sure to select the canonical domain you prefer.
Specify whether you prefer “www” in front of your domain name or not.
If you don’t, Google might see the www and non-www versions as separate, meaning you’ll have shared credit for pageviews, clicks, backlinks, and engagement between two domains. This is disadvantageous for your SEO.
Replace metatags and monitor the impact of CTRs.
Always focus on the CTR of your top keywords and pages. With your internal data, you will see that when there is a constant increase in CTR, the rankings will gradually improve.
Update the title tag and meta descriptions monthly and test to see if these changes can improve your CTR. It is essential that you also perform organic search testing by featured snippets. This strategy can help you increase your overall traffic.
When you are in Google Search Console, click on Performance, and filter the list of queries by Impressions. If you find a query that has a lot of impressions, but few to no clicks, it’s most likely a keyword you’re about to break through and just needs a bit more optimization.
You can flesh out the article a bit or try to optimize the title and meta tags. These are simple methods that allow you to get an idea of certain articles to optimize. So you could increase traffic to your site.
Watch closely for keywords with high CTRs.
By tracking your website in the SERPs, you need to watch out for keywords that have a high click-through rate and optimize your content around them.
If you are optimizing around two different keywords, you might find that one of them has a higher CTR, which can lead to more clicks. This keyword may be more favorable even if it has a lower search volume than the others.
It is recommended to optimize and develop old blog posts using keywords that are already working.
Filter your queries by page and find out which terms are already ranked on the blog. Look for relevant keywords that rank in positions 8-20. Edit your article and use those terms to develop your content and improve your rankings.
It is advisable to post new content at least once a week. That’s a significant amount of content to watch out for with this tool.

When you know which keywords you are ranking for, you can optimize your site to rank better by matching your content to the targeted keyword. Besides, you can also track words that have low CTR and want to rank higher. When you know which keywords have a low CTR, you can improve them.
This is a very good strategy if you have the first and second position pages.
Find optimization opportunities for those in 3rd position or below, by clicking on the query and going to the Pages tab. You will then see which page is ranked.
Check if you can optimize this page by creating new links, expanding the content, or improving the CTR by changing the title and description.

Find interesting topics.
Use the console to spot upcoming trends. You can use the search results performance report and filter to the most recent dates to see where new organic traffic is landing.
Plus, you can look at CTRs, Impressions, and Average Rank to predict where traffic is going to arrive soon.
This information will allow you to check your page’s keyword targeting, evaluate text, improve navigation, and increase link count to take advantage of a new, more popular homepage.
Identify the questions people have about a service offered and use these questions to improve content with FAQs, CTAs, and more.
Here are some steps you can take.
- Open the performance report.
- Go to the Pages tab.
- Sort by Impressions (top to bottom) and see which pages appear the most in the SERPs.
- Click on one of your important pages.
- When the report reloads, click Queries.
- Change the date and click Compare, then Compare the last three months to the previous period.

The key is to find those queries that are at the top of the impression list in the past three months but haven’t generated as many impressions in the past three months. Find those that may indicate that the page is ranking for new queries, or that these new queries are increasing in search volume, and which could represent new traffic opportunities.
It is better to export the data to a spreadsheet and calculate the change. Then sort by change value. So you will see the biggest movements (up or down) over time.
Mix this insight with your click-through count to see if impressions turn into more clicks or traffic. This is an indication of whether your ranking is improving or maintaining. It’s also a good way to know that if impressions have gone up, and not clicks, positions might be going down.
Compare your data to that of your competitors.
Always remember to compare your results to those of your competition.
See what tactics are used if they rank above you in searches. Watch what they are doing that you are not doing.
Benchmark their SEO strategy and do better.
Check your conversion rate
Focus on the customer’s needs and highlight the call-to-action. Build your SEO around the principles of customer service to get more conversions.
Take a look at your conversion rate, user experience, and user journey.
Monitor your most popular backlinks.
In terms of SERP position, you can use backlink tools to look at which sites are linking to you and how much traffic they are generating.
Compile the data in a spreadsheet, including not only the total number of links but also the domains from which the links originate.
Next, you need to look for sites similar to those that already link to yours.
Check their position in the SERP and if they’re indexed, and see if you can come up with a post for their blog or any other content for their resource page.

Identify the links on the site.
Use the Google Search Console to find links from the site that Google deems relevant to the main query.
They are great additions to your SERP result because they give your visitors more options to visit more in-depth pages without having to navigate to your home page. If you can’t find any site links, keep adding relevant content. Do this until your site has enough for Google’s algorithm to take them into account.
Look for internal linking possibilities.
Find the pages that need an internal link. Click on more under the linked pages at the top and then select the internal links.

Internal links can help your new page get indexed faster. Internal links will transfer PageRank to the new page, which could help improve its ranking.
Monitor the SEO performance of a new website.
A new website may not have traffic. However, you can still track the progress of your website by checking impressions in the Google Search Console.
If impressions are continually increasing, it means more keywords are showing up in the SERPs. This means that clicks and traffic are heading to them.
When impressions flatten out and you’re almost out of traffic, that means you need to do something else to get your site up and running.
Measure your search performance.
Look at your performance over time.
It’s a good idea to monitor your website’s average position in the SERPs every month. This information will tell you whether your SEO efforts are working or not.
If your average position increases, it means that your efforts are not in vain. On the other hand, if the average position decreases, then you need to re-evaluate your SEO strategies.
You can also check the last seven days of each homepage to see if the number of clicks and impressions is increasing. Thus, you will have an accurate average of your position over this period.
Remember to use a date comparison for queries. A keyword can have a great CTR, but a higher CTR from a previous month indicates that there is work to be done.
The performance report will give you a great indication of the health of your website and will tell you where to start when improvements need to be made.

You can also compare annual or quarterly performance.
There are several lessons you can learn from this, including checking current rankings and positions compared to the previous period, as well as clicks and impressions. It also gives you a good idea of your click-through rate.
Even if you have much better rankings and stronger impressions but a low CTR, there is a need to correct your CTAs or meta titles/descriptions. You should also take a look at what you are doing on other channels so that you can capitalize on “missed” opportunities.
Check which keywords and pages are getting high impressions but low clicks, then work on your SEO to increase page/keyword rank.
You will then be left with the third column which will tell you the “difference”. Toggle this column to see which pages gained the most visitors and which lost the most.
This tells you what works and what doesn’t and which pages have the most significant changes in the SERPs.
Be aware of your audience, because the way they use your site will create a domino effect that will have a direct impact on your strategy. See how and why visitors are on your site, where and when they leave it, and how to answer their questions and close the funnels.
Collaborate with your team.
Most companies only have one person to manage their SEO and that is often far too little.
Carefully review your research report at the end of each month, work with your team, and watch out for queries that get a lot of impressions but few clicks.
High volume, low CTR searches indicate that if you have a page that ranks for your search words, it is irrelevant. It is, therefore, necessary to write a highly targeted page for these queries, in collaboration with your team.
Use the Search Console to make sure the right page ranks correctly.
Keep in mind that Search Console data is not perfect.
One of the best ways to maximize the use of Google Search Console is to view the data using another tool like Data Studio.
Experts agree that the overall average position should not be used as a KPI.
When Google measures the average keyword position, it looks at the top 1,000 SERP spots. This means that if you gain new keywords, but rank at the bottom of the scale, your overall average position will decrease.
You can think of the average position as a KPI if you do it keyword by keyword. Even so, experts say this is not an essential metric when you consider the difference in click-through percentage between keywords.
What you need to pay attention to is what organic click triggers are. For most websites, these are usually the first thirty Console requests. You should optimize the pages that rank for these queries.
An extremely high impression count is a red flag. Try filtering by impressions and see which pages are viewed but not clicked. Maybe their content is irrelevant, or the SERP listing isn’t exceptional. Both of these assumptions are SEO issues and you should address them at the same time.
Another expert tip for using these tools is that you should understand their limitations and avoid expecting them to do what they cannot. The GSC is perfect for regularly tracking the positions for which your website has been found on the SERP by keyword.
One of the keys is to understand the user engagement on SERPs with the website. The tool is particularly of little use in understanding what users do after leaving the SERP.
Detailed and in-depth tracking is needed for a more in-depth study of user engagement.
Look for internal linking opportunities to improve rankings.
Systematically take advantage of the Google Search Console to create internal links. You’ll see almost automatic results when you link pages with authority to pages you want to rank higher.
This tactic is great for getting your site on the first page of Google.
Look for pages that rank in 4th and 9th position, and find the high authority pages on your site by sorting the pages by impressions and clicks. There you will usually find the most popular pages for Google.
After you identify your high authority pages and your underperforming pages, link the high authority pages to the lower performing pages. In doing so, some of the authority of the high authority pages is shared with the less performing pages. This allows your underperforming pages to gain prominence in the rankings.
Find out which pages are wasting your budget.
Google doesn’t always crawl your every page. Sometimes he has a crawl budget that limits the number of pages he crawls regularly.
This is a potentially vital problem, as it could cause Google crawlers to ignore your new content or updates.
For small websites, a crawl budget is usually not a problem. However, pages with thousands of pages can have a downside. When you have a large number of low-value URLs, they can hurt the crawling and indexing of your website.
Use the Google Search Console to find low-value pages that can negatively impact your crawl budget. This tool is useful for finding unvisited pages.
Look for the pages that get the lowest number of impressions and clicks. You can choose to delete them, redirect them in 301 to pages with similar content, or update their content.
Studies show that when you delete pages with little or no traffic or redirect them to significantly better content, Google adds more value to relevant pages. This method greatly increases the traffic to your website.
Identify the main target keywords.
When you already have a lot of content, you should probably review your existing pages and find out if there are opportunities to improve rankings on specific keywords. It’s common to make mistakes when choosing keywords the first time.
You need to get the perfect keyword for any content you posted and then improve and re-optimize the page with a better keyword. To do this, you need to discover your page’s ranking queries along with impressions, its click-through rate, and average position data.
Sort by impressions and find which query has the most impressions that rank in positions 3-7. Add this query to the SEO or H1 title of your page.
According to experts, these simple changes to metadata and page content can take you from page 2 to page 1. Within two weeks of implementing the changes, you will likely get the traffic you are looking for.
Look for opportunities to improve your CTR.
The click-through rate is a very important ranking factor. If your result has few or no clicks, you will lose your place in the ranking because Google will consider your result to be irrelevant. On the other hand, if your result has many clicks, your ranking will increase.
Focus on your CTR on the queries and pages you’re already ranking for. If you have impressions but don’t have clicks to your page or article, all you need to do is spend a few minutes figuring out how to optimize your title, meta, or URL to get people to click on your content.
Watch the other pages that rank around you and ask yourself some essential questions.
- Does the content of the page match the search intent?
- Does the title represent the quality of the content?
- Is other content better than mine?
- Do I anticipate and answer my readers’ questions?
You need to create attractive title tags that intrigue readers. Include numbers and parentheses to make the title appealing to a wider audience.
You should also make sure that the meta description explains why readers should click on your content rather than other people’s.
Look for pages that require additional optimization.
The tool is the best source of data when it comes to page rankings. Whether you get the insights indirectly from reports fed into Google Analytics or directly from GSC, you’ll have great insights into your SEO.
Find a page that ranks and see what level it ranks for, for which phrases, and improve its optimization. It is one of the fastest ways to improve search traffic.
Find keywords that rank on page 2 or at the bottom of page 1. Keywords that have great impressions but rank lower are essential keywords that require your attention. They can potentially generate great traffic.
Use analytics to see which pages are getting the most traffic, and use the console to find data you can use to optimize pages even further.
Find out which terms rank on each page and which are between 2nd and 10th position in search results. Focus on these elements. As long as they are relevant, you can take those words!
This is a great optimization method for historic blog posts that may attract some organic traffic, but perform poorly given the high quality of the content.
Find keywords to target in paid campaigns.
This tool is an incredible source of keyword ideas and ad copy suggestions. It’s also a gold mine for the best landing pages for your Google ads.
Configure your performance report to show clicks and impressions for all cases with the “Last Three Months” timeframe. After that, sort by impressions, and you’ll find keyword ideas for your ad campaign.
Select “Average CTR” and “Average Position”, then sort by position to see which search terms your pages rank highest for. Use this combination of homepage and keywords to increase the chances of getting a better quality score for your ad group.
When you get a higher quality score, it means you have a lower cost per click and a higher position.
Find new content ideas.
You can export up to 1000 found queries. Export this data and categorize queries by subject or category to understand the keyword groupings that appear on your site.
The data will tell you which areas you need to spend more time to get more impressions or clicks in organic search. You’ll also get ideas for topics you can write articles about that will help increase your traffic and improve click-through rates.
Measure the evolution of search volumes with and without brand.
The Google Search Console has an extensive keyword database. This data is one of its most widely used characteristics.
The tool goes way back in time, which is useful for tracking and evaluating the performance of keywords year over year, whether or not they are branded. This results in a more precise data set.
Decrease the bounce rate by researching negative keywords.
Using Google Search Console, you can know your site’s ranking for keywords so that you can identify negative keywords.
Negative keywords are queries that you rank for but have misplaced intent. Inappropriate keywords will have a negative impact as they affect your bounce rate.
You can reduce your bounce rate by fixing the problem with appropriate corrective measures.
One way is to update your content to more accurately respond to keywords that you rank for but haven’t covered in your content.
Another way is to create new content that deals with the intent of a negative keyword and link it to the existing article.
Give Google additional information without adding structured data.
Add structured data to your site to give Google more insight into your content.
You can use structured data to specify whether a piece of content is an article, FAQ list, recipe, or review.
Structured data helps Google better understand your content, and it can help expand the list of search results.
For example, this is a search result that has structured data for both a recipe and ratings. These two types of data provide a more detailed search result:

Keep in mind that not all SEOs are experienced in web development. Often, even SEOs who are proficient in code do not have access to essential website code.
By using the data highlighter in the console, you can customize how a site will appear on search results pages. This allows pages to stand out, improve their rankings, and contain more context to give Google insight into your content.
The data highlighter makes it possible to mark different contents on a website without adding structured data to the code. You just need to choose what item you’re going to highlight, whether it’s reviews, software, or restaurants. Then enter your page URL, and start highlighting.
Once you’ve highlighted content, you can continue to add other information about it, whether it’s an official URL, an image, or a download URL.
Google ranks items based on contextual clues. Using the data highlighter is effective in enhancing the context of your website content.
Use other tools besides the GSC.
If you continually optimize your site for SEO, you will find time and time again that you need more data to go deeper!
You will need essential data from Google Analytics and Google Search Console, even if you are only doing basic SEO.
As you progress and improve in practice, it would be helpful to use data from other popular SEO tools like SEMrush, AccuRanker, Moz, and Ahrefs.
One way to consolidate this data is to connect the Google Search Console with Google Analytics. When you combine these tools, you have access to keywords and search performance data.
Databox is another option. It’s a data visualization tool that lets you create shareable dashboards that centralize information from over 70 tools, including Analytics, Console, Ahrefs, SEMrush, AccuRanker, and Moz.
