An invisible site is a useless site. And to be seen, you need to make sure Google finds and indexes your site correctly. Not once, but every time you post something new. This is where technical optimization comes in to make your site visible to search engines. How and how do you know if Google sees you?
Without indexing, no traffic, and no visibility
Obviously to start this article: when you publish a new site, it does not announce itself to the search engines. These are crawlers (called crawlers or bots) that do the job and find it. As a reminder, these robots crawl billions of web pages all day long, following internal and external links to index and organize all the content they find.
Google’s index is a gigantic database that functions as a library. When you search for information on a given subject, Google digs through its catalog (index) to provide you with a list of relevant data (ranked according to its algorithms). This leads to the results page you are familiar with (the SERPs – search engine results page).
Google builds its index by analyzing and saving ( indexing ) multiple information on each page visited ( crawling ), then by storing them in its index.
So no matter how much time, energy, and money you spend creating “the perfect site,” if your site isn’t indexed, Google can’t display it. Your visibility and your chances of getting organic traffic are therefore zero. To fully understand how Google organizes the information it finds on the net, I invite you to watch the video by Matt Cutts.
Check the presence of your site on Google
The fastest and easiest way to check if your site is visible, and “indexed” correctly, is to ask Google to list all of the pages it has indexed. With the following syntax:
site: example.com
(replace example.com with your site url – without http (s), without www, without space)
You will thus know precisely how many pages are indexed by Google (or Bing or Yahoo). This can also vary from day to day, depending on the passage of robots.

You can then compare these results with the list of pages on your site. Google’s webmaster tool, the Google Search Console, summarizes the situation for you:

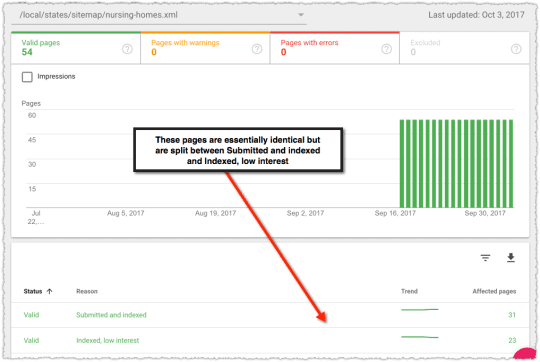
As you can see the pages and images are indexed separately. Both can bring traffic to your site. Hence the obvious interest in optimizing your images.
My site is not indexed, why?
If your site is not indexed, there could be several reasons for this.
Help! My site is invisible.
If your site is brand new, Google bots may not have detected it yet. But if it has been around for some time (weeks/months) and if Google has not indexed anything, it is because it does not see it. The most common reasons are technical:
- An htaccess file is blocking the site. It is a configuration file for Apache HTTP servers.
- A robots.txt file is blocking indexing. This file communicates specific guidelines to Google robots regarding crawling, accessing, and indexing content. For example, if it contains a <noindex> tag, Google will not index your site.
- WordPress settings prevent indexing (which is a common practice in the pre-production phase, to avoid showing a site under construction).
- The quality level is insufficient. Google may crawl your site and decide not to index it. If your site is rated as low value, has little content (or no content at all), Google may decide not to index some or all of your pages to maintain its standards.
When will your new site be indexed?
Knowing when a new site will be indexed is a question that cannot be answered with certainty. Because even if everything is done correctly, strictly following the guidelines provided by Google, it depends on factors beyond your control.
Since crawlers crawl billions of pages all day long, and they have to come back to them regularly to keep their information up to date, we understand that there can be a certain amount of time between the moment you publish your site and when Google (or Bing or whatever) crawls it: a few minutes, a day, a week, or even a few months in some cases.
But there is a way to accelerate this process as we will see later.
Some pages are not indexed, what to do?
If one or more pages are missing, review the list of indexed pages and identify those that the search engine did not include. Here too several possible reasons:
- Presence of certain meta tags – Evaluate pages that are not indexed to make sure they do not have the <META NAME = “ROBOTS” CONTENT = “NOINDEX, NOFOLLOW”> meta tags. This particular meta tag prohibits robots from accessing the page, which in turn prevents the page from being indexed.
- a duplicate content problem, or low-value content.
- A technical problem, linked to a reference to a 404 page or a loading problem.
- A faulty internal mesh: check the URLs of your internal links
Diagnose indexing problems
If the crawlers cannot find your site, after checking the points I just mentioned, consider (having) create a complete XML sitemap (a list of all the pages to be indexed), which you will then submit to Google, to help it discover your web pages.
If your site is indexed, there is probably still room to improve its indexing. The importance of good indexing depends of course on the type of site or page concerned. Logically, a poorly indexed e-commerce site is much more critical than an inconspicuous personal blog post. Especially since organic traffic is the most profitable form of traffic for businesses (since it costs nothing). You might as well optimize it to the maximum!
Find and fix technical errors
As a reminder, the main sources of blockages are technical :
- Incorrect configuration of the robot.txt file
- Error in .htaccess file
- URL errors (404 errors, access denied, URL not tracked)
- Connectivity or DNS issue
- Lack of sitemap
Don’t forget to index all (sub) -domains
- If you switch from HTTP to http, you change the domain. In this case, the pages on your site are indexed as https://example.com instead of http:// example.com. To keep Google from not finding you, be sure to set up 301 redirects from the http version to the https version of each page so that Googlebot (and people on the Internet) know where to go.
- Likewise, make sure that versions with or without www are properly indexed. Indeed, for Google, example.com and www.example.com are two distinct URLs that can present different contents. That’s why it treats these two URLs as two separate sites in Search Console. Configure correctly to avoid duplicate content.
- Finally, your site may also be located in a subfolder, especially if it is hosted on a free platform (www.example.com/rollergirl/).
Correct reading errors (crawl)
Sometimes certain links lead to non-existent or out of place pages. Your site then has a multitude of reading errors ( crawl ). You can identify them using the Google Search Console.

Analyze the Index Coverage Report
This Google Search Console report helps you fix all indexing errors. The graph represents the total number of URLs known to Google, and in the case of excluded URLs, details why they are: anomaly, redirect, not found, “noindex” tag, etc.
For more explanation, see the Google Index Coverage Report page.

For a site visible quickly, help Google
You will understand, to correctly analyze what is happening on your site, start by installing Google Search Console.
Speed up indexing with a sitemap
To speed up the indexing process, first, submit your sitemap (sitemap) to Google through the Google Search Console. Because even if the sitemaps do not influence your “ranking” they will encourage Google to index your site faster and more efficiently.
Have you created the page or requested indexing recently? Google may take a long time to index your page. Allow at least a week to pass after submitting a sitemap or index request before considering the possibility of a problem. If the changes to your page or site are recent, wait a week before rechecking if they are present in the Google index.
Remember to keep your sitemap up to date on Google Search Console. Drop by once or twice a month to check out what’s going on at GSC.
Optimizing your website for indexing
To ensure that indexed pages remain properly indexed, that new pages are added to the list, and that unwanted pages are not included, it is important to regularly review the following:
- Take care of the ergonomics of your website. Does everything work as it should from a technical point of view? Is the server handling the load as it should?
- Improve your internal mesh. Do you have enough internal links to encourage regular crawling? Multiply the links from one page to another (but without overdoing it), this is useful for search engines but also to keep your visitors longer on your site.
- Use breadcrumbs. Are the pages correctly nested and placed in the correct categories? Maintaining a logical internal structure is very important in showing search engines that your pages are worth indexing.
If you want to drive quality traffic to your site, then you will need to familiarize yourself with all of these concepts or consult someone who knows exactly how to check these things out and make the necessary changes.
Some tips to boost the indexing of your site
Post regularly
Content creation is one of the two most important ranking factors in the SERPs. If your site has been running for some time, to maintain a good level of indexing, the best recipe is to regularly post new content or update old content. Because the more you update your site, the more Google robots will pass to check for new features.
Practice link building
Robots access your site through links. There are many ways to generate links that point to your site. You can do this by writing articles or posting comments on relevant websites. You can also create links to your site on your social profiles (Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn). Or display the photos on your site on Pinterest or Instagram, create videos and upload them to YouTube, presentations on Slideshare, adding a link to your site in the description each time, etc.
Clean up your website
Certain elements of your site can decrease the crawl rate, such as duplicate content, unnecessary pages, certain images, etc. Use Robots.txt files to tell robots how to crawl the pages on your site and prevent them from indexing irrelevant pages. Optimize your images for inclusion in search results by installing the Google image sitemap plugin.
Use a server with a good level of availability (uptime)
When you host your site on a reliable server that does not experience regular downtime, your site is accessible to Google robots at all times. As a result, bots will increase their search rate, and your site will be indexed faster.
Another recommendation: optimize the loading speed of your site. Google has no time to waste! The faster your site, the better the indexing. Also, Google favors fast sites because they offer a better user experience.
Share and promote your site
Another very easy way to get links to your site or blog is to submit your new URL to online directories (business, local,…). This tactic is of course useful in getting your site known to potential customers, but it can also help speed up indexing.
Some pages should not be indexed
Some pages on your site should not be indexed. For example, utility pages. You can ask Google not to index pages such as:
- The “admin” and “login” pages: these pages should not be indexed.
- The cart pages, account creation, authentication, lost password, etc . in an e-commerce site.
- Media pages – on WordPress, these pages may dilute the quality of your indexing
- Thank you pages: These are the pages you land on after signing up to a mailing list or downloading a white paper. If these pages are indexed, you could lose leads since they no longer have to fill out a form.
- Internal search results – linking to a search page is the best way to spoil the search experience for internet users.
- Duplicate content – the site is accessible with or without www; articles accessible via different URLs, A / B testing pages; pages with very similar content (for example, variations of the same product on an e-commerce site); the printable version of a web page. In all of these cases, the different versions do not need to appear in the search results. Keep only one page indexed

source: Neil Patel
If you have an e-commerce site, with hundreds of thousands of products, indexing unimportant pages can become a problem, because you want Google bots to focus on the important pages.
To find out more, I invite you to read Neil Patel, who explains why not indexing some less important pages can help you get more traffic.
