Internet users reveal a lot of information through their surfing behaviour. Publishers, advertisers and marketers, in turn, use this information for behavioural targeting to increase the relevance and effectiveness of advertisements and marketing messages.
Before web tracking technology made this form of targeting possible, marketers acted more with a watering can than with a magnifying glass in their advertising efforts: advertising messages were distributed without analyzing users’ interests or actual behaviour.
Behavioural targeting helps marketers avoid wastage and unnecessary expenses in online advertising and show users the content that interests them. This post will show you what behavioural targeting is, what types there are, and how it works in general.
What does behavioural targeting mean?
If an Internet user’s surfing behaviour is decisive for which advertising is shown to him online, one speaks of behavioural targeting or behavioural targeting.
With behavioural targeting, advertisers use user behaviour as the basis for displaying content and advertising that is relevant to them.
Search engines like Google and Bing demonstrate every day how effective this targeted advertising is. Search engines use keywords as an indication of the user’s intent.
Behavioural targeting tries to increase the relevance of advertisements using as much data as possible about prospective customers’ online behaviour and potential customers.
For this to work, users who have visited certain websites must be identified again when they see another website or the same website.
Cookies and anonymous user profiles are used to identify different users.

One of them is behavioral targeting
The use of cookies in behavioural targeting
Cookies collect and save information about internet users, e.g. which pages they visited and which interactions they carried out on the website. Cookies can be placed in a website visitor’s browser in two different ways.
When a user visits a website, the cookie can be generated by a script integrated into the website and stored in the user’s browser. Alternatively, the cookie can be sent directly from a web server to the user’s browser and saved.
This information collected by cookies can be retrieved each time the same user visits and linked to the user profile.
A distinction is made between two different types of cookies. Cookies generated by a website and only save the data within their website are called “first-party cookies.”
With behavioural targeting, however, user behaviour is usually saved and analyzed across several pages. For this purpose, so-called “third-party cookies” (third-party cookies) are used, which are integrated by advertising service providers into websites that work together with the advertising network.
The disadvantage here is that users can block the tracking of their activities through third-party cookies in their browser’s data protection settings.
Creation of individual user profiles using cookies
The cookies stored in an Internet user’s browser collect and transmit detailed information. For example, about the actions carried out by the user, products viewed, and websites visited.
The operator of a website or an advertising service provider can collect and use it to create a user profile.
Depending on how detailed the data is, it enables conclusions to be drawn about individual users’ interests, leisure activities, or purchase intentions.
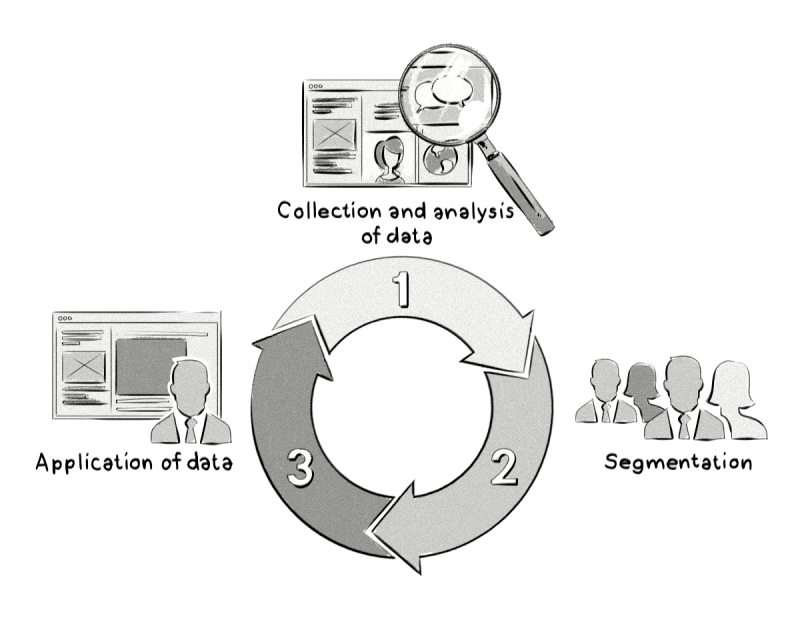
Based on this information, the various users are assigned to specific groups (segmented) to be shown customized advertisements in the future.
Depending on the type of behavioural targeting, the advertisements are delivered on your website or another page of a more extensive advertising network such as B. Google Ads.
What types of behavioural targeting are there?
There are two types of behavioural targeting: Onsite and Network Behavioral Targeting.
Onsite behavioural targeting
Onsite Behavioral Targeting is behavioural targeting on a specific website. Ads are displayed to the user based on behavioural data and other information about them collected on the same website’s pages.
As the operator of a website, you can use analysis tools such as B. Use Google Analytics or eTracker to create detailed user profiles of the visitors to your site.
These analysis tools use a so-called tracking code integrated into the source code of your website.
This tracking code enables tracking and comprehensive analysis of visitor behaviour. However, website operators who are active in Germany must observe the data protection regulations of the GDPR, which were tightened in May 2018.
With onsite behavioural targeting, it must therefore be ensured, for example, that the personal user data is either recorded anonymously or that the users have given their consent to the creation of user profiles.
Network Behavioral Targeting

Network Behavioral Targeting describes the targeted placement of advertisements in an advertising network. Advertising marketers such as Google, Facebook or Taboola combine many online platforms into comprehensive advertising networks.
The so-called display network from Google can be used by every website operator to place advertisements.
According to statistics from WordStream, the display network now comprises more than two million websites. It reaches around 2.5 billion internet users worldwide every month and generates more than 2 billion ad impressions. Madness!
Other providers with a lower range usually only work with a few selected partners. Google DoubleClick, Ad Pepper, TradeDoubler or Facebook act as marketers and intermediaries between advertisers and publishers in the advertising networks.
The websites’ owners in an advertising network provide advertising space on which the marketers publish their customers’ advertisements.
With network behavioural targeting, the advertisements are centrally managed on and distributed by ad servers.
Advertising networks reach large parts of the Internet. Detailed analyzes by the operators provide a comprehensive picture of the online behaviour of potential customers.
The user data collected on the partner sites of the advertising networks are managed centrally and can be used by advertisers to target their campaigns throughout the system.
If a finely differentiated user profile is created for each user, it is called microtargeting. Microtargeting is about placing an advertisement or sending an e-mail, possibly only based on a single trigger.
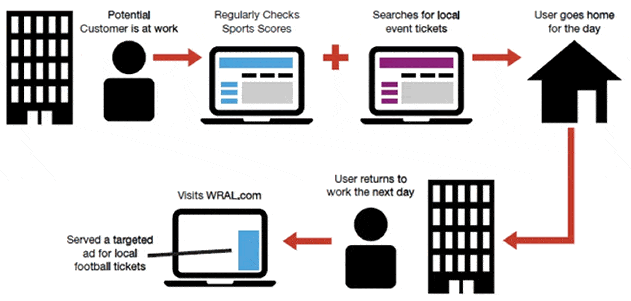
Microtargeting plays a role, especially in retargeting. Retargeting means are addressing users repeatedly, e.g. B. A website’s visitor showed an interest in buying a particular product, but no conversion has taken place.
Using retargeting, the visitor is addressed again at certain intervals and reminded of his / her intention to purchase the product or the service.
Predictive behavioural targeting
Predictive behavioural targeting is another variant of behavioural targeting. With predictive behavioural targeting, specific attributes are assigned to anonymous user groups based on statistical forecasts to predict user behaviour.
These include, for example, socio-demographic factors such as age, gender, income and education. Other factors are psychographic characteristics such as purchase intentions, knowledge and interests.
The data used for predictive behavioural targeting can come from several sources, including websites, mobile apps, customer surveys, CRM systems, and other marketing automation systems.
In addition to statistical data, so-called click stream analyzes and data mining methods are increasingly used for predictive behavioural targeting to search a continually growing amount of data for trends.
The goal of predictive behavioural targeting is to create so-called personas (statistical user profile) used to classify website visitors.
What are the goals?
Behavioural targeting aims to avoid wastage, increase conversion rates, and thus increase advertising campaigns’ success. Taking user interests into account is the key to successful advertising campaigns.
If internet users are presented with relevant ads in the right place at the right time, they are more likely to convert the ad.
A goal of behaviour targeting can, therefore, be to reduce the CPA (Costs Per Action) and consequently, an increase in the ROI (Return on Investment).
Placing relevant ads also improves the user experience, as visitors to a website can find the information they are looking for.
What are the advantages and disadvantages?
The advantage of behavioural targeting is the ability to place targeted and relevant advertisements that are rarely perceived as annoying and helpful.
With network behavioural targeting, advertisers can track their potential customers across the entire network and offer the right products or services. A dream for every marketer!
A disadvantage of onsite behavioural targeting is that collecting user data and creating user profiles involves an individual effort. Every user profile must be maintained and updated regularly.
When using an advertising network, marketers take on this task. Both onsite and network behavioural targeting always reach their limits if they are to be implemented following data protection guidelines.
Another disadvantage is that the behaviour of users who do not allow cookies to be placed cannot be tracked—likewise, the behaviour of users who delete browser cookies when closing cannot be followed.
Examples of behavioural targeting in online marketing
Examples of the application of behavioural targeting are, e.g. B .:
- Cross-sell and up-sell offer as found on every Amazon product page.
- Behavioural email marketing, in which emails are automatically sent based on a website visitor’s action, is also an example.
Google and Bing use behavioural targeting methods to increase their advertising revenue. For this purpose, Google uses data from the web protocol, the Google account as well as Google Docs and Gmail to find out more about the users to analyze their behaviour and to be able to place targeted advertising.
Conclusion: annoying for some, indispensable for others
With the methods of behavioural targeting, marketing channels and topics can be linked. The collected data and individual user profiles show what interests the users have, what they are looking for and what they want to buy.
With targeted advertisements, the wishes and interests of Internet users can then be addressed without significant wastage.
Thus, behavioural targeting makes it possible to significantly increase the efficiency of advertising campaigns, improve the conversion rate, and reduce costs.
In this sense: Happy targeting!
