How can you create your link portfolio? What do you have to pay particular attention to when evaluating or assessing? And what about the disavow file for Google?
If you want to have your backlinks under control, you have to deal with the topic of backlink audits.
Purpose of the backlink audit
A backlink audit is a larger or smaller matter depending on the number of links and the quality of the linked pages. Why should you bother to invest in this activity in the often tightly calculated time, work and resources?
The main reason can be summarized quickly and easily: You do not influence all the links that are set!
It is essential to know the links that others post to your website. It would help if you always kept an eye on where your page appears and what exactly is linked. Links created naturally are, in most cases, not a problem. For example, if it is a website that introduces a new lifestyle product, many interested influencers will set a link to it. You can monitor this yourself to a certain extent and, if necessary, start outreach campaigns to make the product better known. However, a lot of links in this area are created by likes, awareness, followers, and other things more incidentally than consciously. Most of these links are nothing to worry about.
During a backlink audit, however, you will almost always come across a spam page or a website with pornographic or harmful content at some point. This article should clarify how to recognize such pages and how to proceed with these pages. But first, it is a matter of analyzing the backlink profile and finding out all the backlinks.
“Does your website have links from porn sites too?”
When or why should a backlink audit be carried out?
It is advisable to conduct an audit regularly. This can be every six months or once a year, for example. If the visibility has changed significantly, you can also use this as an opportunity to examine your backlinks. This allows you to recognize backlink spam and intervene directly.
Determine the backlink profile
To start with a backlink audit, it is essential to identify all backlinks using various tools. Most tools offer the option of exporting a file with the relevant data. In the end, all data is brought together in a master table, and this list is then used. Since the exported lists are in CSV or XLSX format, it is most comfortable to work with an Excel list. This forms the basis for the explanation of the procedure for the backlink audit in this article.
Compile data for the master table
To create a comprehensive master table with as few gaps as possible, you should pull the backlinks from various sources. There are a lot of different tools and possibilities, a small selection of which are explained here for this purpose. Different tools are used, as there are various sources and procedures for determining the data. It is possible that one tool only finds links that are still online, but another also outputs the links that are offline or for which the actual website has been redirected to another. For this reason, data is best drawn from various tools. How to avoid duplication is explained at the end.
1.ahrefs.com
This online tool offers a lot of data regarding backlinks. To get the relevant data, you first enter the domain that you want to examine. You get a first overview directly, in this case, the 120M backlinks using the example of Wikipedia (Figure 1) are impressive. You can take a closer look at these in the next step.

Figure 1: ahrefs.com overview Wikipedia.org
The “Backlinks” category is located under the “Backlink Profile” menu item. This contains the information required for the backlink audit. To ensure that the table you are looking for contains as much data as possible, it is essential to click on “All links” in the options. Otherwise, a link is issued per domain, which is sufficient in some cases. Still, if you want to view the entire profile, you should look at the individual links and, in the best case, evaluate them individually.
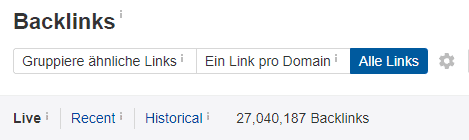
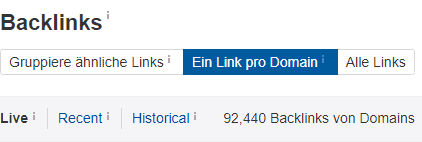
As you can see in Figure 2 and 3, the number of backlinks varies enormously depending on the selection of the option. The example from Wikipedia shows that on the one hand, there are over 92,000 hits; on the other hand, there are over 27 million. Evaluating all of this individually is of course almost impossible or only takes a lot of time, spread over several shoulders. Wikipedia.org is an example that, of course, has a lot of backlinks. A website with an average reach has significantly fewer backlinks. In most cases, the backlinks are in the 3,000 to 100,000 range.
Once this data has been determined, all you have to do is export it. Figure 4 shows that you can differentiate between fast and complete export. The total shipping is always preferable, as it contains all the backlinks that the tool has previously found. After clicking on the “Start the export” button, you have to wait a certain amount of time, depending on the number of links, and then you have the finished list.
2.SISTRIX
Another tool that can be used to determine the backlinks of a page is SISTRIX. With a click on the “Links” button, you can also get an initial overview. Figure 5 shows this overview, which initially shows the number of backlinks, and to the right of it, you can see the current development in the link profile.
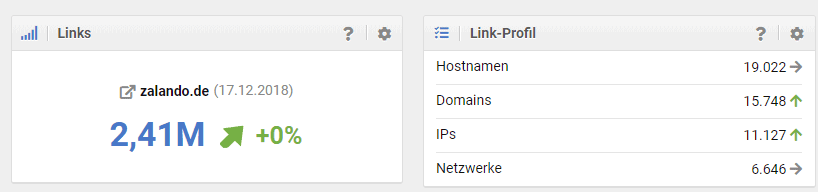
Figure 4: Links from zalando.de via SISTRIX
The individual links are then output under the “Links” option, which can be exported as an Excel file, as with ahrefs.com. If necessary, you can set different filters. However, if you want to show the complete profile, you should not limit it here either.
The same applies to the actual export. Here the full export is automatically set, nothing should be changed. If necessary, you can adjust the file name. It is recommended that you name the files after the respective tool. As a result, you end up with various Excel files, with which you can always trace back at a glance where you got the data from. It is easiest if you name the files according to this pattern:
“Name of the website_date_tool”, e.g. B. “zalando.de_20.12_SISTRIX”
This is particularly helpful when you create the master list at the end and can thus find out more easily which files you have already copied or integrated. You can also see directly from which tool you have already exported the backlinks.
3. LinkResearchTools (LRT)
Another well-known tool is provided by LRT. There are two options for creating the master table: a complete and a quick export.

As can be seen in Figure 5, there are two tools: the Backlink Profiler and the Quick Backlink Checker. The backlink profile is used to get the most backlinks from this provider. If you have clicked on this, various options are offered. You can select different metrics that are relevant to the audit. Also, you can set how many backlinks are issued per website and whether you want to work on a domain or URL level.
4.Other tools and resources
Additional sources can be used for these three important tools as required. One of these relevant sources is the Google Search Console. After a successful link, domains are output here, but this is not as extensive as with the other tools.
SEMrush should also be mentioned at this point. A new project must first be created here so that data can be determined. Once this has happened, select the “Backlink Audit” option (see Figure 6). The number of linked domains is shown directly. After a short waiting period, another Excel table is available here.
The first step has now been taken. Once all the data has been recorded, saved and correctly named, it is time to create the master table.
Create the master table
To generate the table with which the audit is carried out at the end, all previously created Excel files are first summarized in a table.
1. Merge relevant data
It is sufficient to use the column with the referring domains. The other columns offer different data depending on the tool, which should not be taken into account in this step. In the end, a uniform table must be created, which is used to evaluate the backlinks gradually.
2. Remove duplicates
Under “Data”> “Remove duplicates”, the table is checked for duplicate entries and cleaned up. This reduces duplication and saves work during the actual audit.
3. Upload file for evaluation In
order to create a uniform file with the appropriate columns, the data is finally uploaded to a proper tool. The Link Detox Tool from LRT has proven itself in practice. SEMrush offers a further option by uploading all data and exporting a general list at the end. However, LRT has the advantage that offline links are taken into account. If you want to take a closer look at them and reactivate them if necessary, LRT provides more data.
4. Create the cleaned table
The entire exported table is now created. For a better overview, it is advisable to name the table with the addition “Master”, for example, “Zalando.de_Audit_Master”. It is advisable to reduce the table to various data before the audit. Depending on what is relevant, columns are deleted or retained. The following areas are essential:
- A column with the linked websites
- A column with hyperlinks from these websites
- A column with the anchor texts
- A column with the links on the examined page (link target)
- A column of do-follow / no-follow
- A column with the rating of the tool (e.g. Toxic Score)
- A column with the status (online / offline / redirect)
- A column with comments (e.g. OK, offline, disavow)
5. Format data
If the table only contains the relevant data, it is advisable to sort them in alphabetical order. If identical domains with different URLs appear in the list, your work is made more comfortable if they appear in a block one after the other. To do this, format the appropriate columns as a table that can be filtered and carry out the necessary step.
So, in the end, you have a clean master table and can start evaluating the links.
Performing the audit – tips for a practical approach
The actual link evaluation is a correspondingly time-consuming matter depending on the number and quality of the links to be examined. However, the following tips should make it faster.
If there are a large number of links to investigate, you can consider whether you are only evaluating each one with a particular risk. Here you have to entirely rely on the tool used and determine in which area you want to examine the pages. With this method, websites with a low risk can be ignored and commented directly with an “OK”.
Which leads to the next point: Never use too many types of comments and do not write them differently. If you mix “OK”, “good”, “positive”, “fits” or the like wildly together, chaos will emerge in the end that should be avoided. Therefore it is advisable to use a few, but meaningful comments. Comments like “OK”, “offline”, “disavow”, “manually dismantle” are sufficient. In the end, the individual groups can be filtered and packed into separate tabs.
You have to decide whether you want to rate the individual URLs or an entire domain. If you look at the area as a whole and look at two or three links, for example, it is faster. It is, of course, more thorough in looking at each link individually.
Anchor texts are another way of quickly arriving at an assessment. These quickly show whether a money keyword (e.g. suitcase, bag, phone) was used or whether the company name is misspelt. It is also possible that the link text says something completely different from the link that is behind it.
How do you recognize “bad” sides?
With many pages, you can see at a glance that they should no longer appear in your backlink profile. The following points should be considered because they indicate the quality of a website:
- How is the site up to date? Is the site actively maintained, or has it “fell asleep” for a specific time?
- Does the website have malicious content? Viruses and malware are to be observed here!
- Does the website contain harmful, pornographic content?
- Does the website offer something, or is it just a list of links?
- Does the theme of the website match your website?
- Do all articles have links to commercial sites? Is the site only there to make money? Some sites publish one sponsored post after another. Such a page is not of high quality because it does not serve the reader or user.
Evaluation of the data and further action
At the end, you have a table in which you have rated your backlinks individually or in a group. The backlinks, with which everything is fine, do not need to be edited further. But what happens to the other links that need additional attention?
Offline links
The offline links are most likely primarily ignored. However, if the audit found links that are important and should not be offline, they can be reactivated. The best way to do this is to contact the webmaster directly and ask.
Dismantling manually
This procedure must always be tried first! You should ask the respective webmaster if you have found links that might damage your website or misdirect the user. Then it is advisable to address the webmaster directly and ask him to change the backlink or take it offline.
Upload disavow file
Last but not least, Google offers the option of uploading links in the disavow tool. If the websites are already known from previous audits or if it is impossible to contact the webmaster, this tool is used. This is done via the Google Search Console in the corresponding area. Google no longer considers the links that are uploaded here. You, therefore, no longer have any influence on the ranking.
Info
The so-called “disavow file” can be used to inform Google which backlinks you want to distance yourself as the operator of a website. The reasons for wrong links on your site can be varied. A (hopefully) former employee may have tried many years ago to improve the ranking through dubious link building. From time to time you are automatically linked by semi-silky portals without even knowing about it. In rare cases, it can also be possible that a jealous competitor has deliberately bought cheap linkspam for your domain and is trying to harm you as a competitor so that you can negotiate a link-based penalty with Google (so-called “negative SEO”). This file is uploaded in CSV format via Google’s Search Console. One tip: It is best not to devalue individual URLs that set unwanted links to you, but always the entire domain. This ensures that there are no further links somewhere on the other URL of the area that the tools have just not (yet) found.
Conclusion
A backlink audit can sometimes be a pervasive project. Depending on the number and quality of the backlinks, this has an impact on the time required. With the appropriate approach, this effort can be reduced, so that at the end of the audit, only the relevant data is available that will be dealt with further. With the help of various tools, the work is made more accessible, and the backlink profile is freed from inappropriate and harmful links.
However, one should not proceed too rigorously during an audit and decide in each case whether a link is harmful or not. The manual procedure – i.e. contacting the webmaster directly – is always preferable, and only if you get stuck here, you use Google’s disavow tool.
It is advisable to conduct regular backlink audits. This can either take place at fixed time intervals or if necessary if, for example, the visibility has changed significantly or Google has rolled out an update.
