For many beginners, search engine optimization is like looking into a crystal ball. Nobody knows precisely how Google or other search engines work. Also, the results of the measures taken are often long in coming.
With this article, I shed light on the situation and would like to help beginners, thanks to their many years of experience, to benefit from the massive traffic through the search engines.

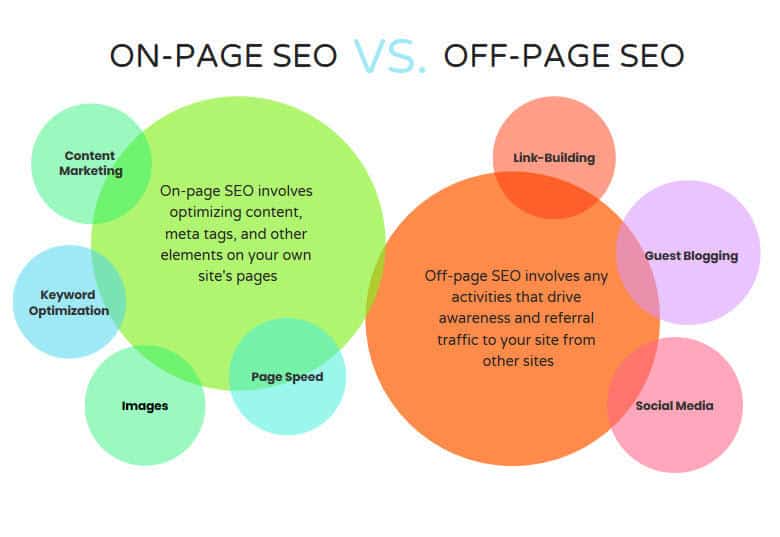
Search engine optimization (SEO) consists of two major areas:
- From all measures on one website ➡️ Onpage optimization
- From all actions related to my website ➡️ Offpage optimization
As can be seen in the diagram below, these are the essential components of programming, content, and link building (and a little social media, whereby the influence is only indirect), which determines the area of search engine optimization. The content creation is linked to both large areas because it plays an essential role in assigning relevant keywords on the website, but also in creating good link-giving content ( link building ).
1. SEO basic rule: the structure of the website
What is worse than sites, the meaning of which is not immediately understood or where it is not clear where the search is found.
But why? The basic structure of a website is essential to get a high level of user satisfaction. Of course, there are also other things in the end, but only if I lead my visitor to the goal in simple steps, do I have a legitimate chance of staying there.
But how does one do it?
The content of a website should be structured logically and hierarchically.
The content or products (in the case of an online shop) should be structured thematically to reflect a good information structure.
A clear information structure is also the basis for excellent visibility in the search engines because the crawlers can better understand and index a page. The Google algorithm will love the transparent structure.
I always ask myself the following questions when analyzing the structure of a website:
- Are the most important pages linked from the homepage?
- Is each category linked to the start page or top and subcategory?
- Can each subpage be reached in 3 clicks?
- Is the path to the respective subpage visible to the website visitor?
- Does the navigation consist of text links?
2. SEO basic rule: A clean URL structure
With a short and meaningful URL, we offer the user a specific orientation. Still, at the same time, we can positively influence the SEO (Search Engine Optimization), i.e., the ranking of the URL. The user can see at a glance what content can be found on the respective subpage.
And the shorter a URL is, the more the words in the URL are weighted. Also, the users of the page can often remember a short URL more easily.
However, there are a few rules that should be followed to maintain a clean URL structure. In contrast to the meta title or the meta description, unnecessary filler words should be avoided, and when using several terms in the URL, it is essential to ensure that the words are separated with a hyphen, as this acts as space.
Also, special characters or umlauts in the URL should be avoided. Umlauts are played with ae, oe, or ue, as they are usually not to be found on the keyboard, especially abroad.
When I set up the URL structure of a website, I always ask myself the following questions:
- Are speaking URLs used?
- Are the URLs used as short as possible / as long as necessary?
- Is the respective main keyword on the bottom listed in the URL?
- Have umlauts been converted correctly?
- Have special characters been eliminated from the URL?
3. SEO basic rule: mobile presentation
Anyone who deals with the topic of search engine optimization or search engine marketing these days cannot avoid the problem of “mobile optimization.”
Every year, the mobile use of the Internet, be it by smartphones or tablets, becomes more intensive, and access via this device increases massively every year.
Of course, the usage varies from industry to industry, but a general trend is effortless to read. Also, the pattern can not only be seen on the go, but the so-called “second screen” in front of your TV is also becoming increasingly popular.
But what is the “mobile optimization” of websites?
Since the Google algorithm also promotes Optimization for mobile content through help in the Google Search Console and mobile-friendliness has been an official ranking factor since April 2015, mobile Optimization of your search engine marketing, depending on the industry, should be given as much attention as the Optimization for laptops or desktop PCs. This applies especially to mobile search results.
In some industries and segments, it can even make sense to drive the “Mobile First” strategy and gradually adapt the content to the technical possibilities of the output device (principle of progressive enhancement). In this way, depending on the available bandwidth, browser, and end device, the user is to be presented with content adapted to him.
In 2016, Google again confirmed that the alignment for mobile devices plays a vital role in the algorithm. The search engine giant has set the mobile index as the primary index of the search engine.
AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages), a format that enables mobile websites to load almost in real-time, was also introduced. These pages have extremely slim source code and are delivered via CDN (Content Delivery Networks).
Also, the “Progressive Web Apps” format is another type of Optimization for mobile devices. With this format, websites can be used almost like standard apps and significantly simplify the innovative usability.
In addition to the Google Search Console, Google provides every search engine optimizer with another free tool that should provide valuable information about optimization potential as part of mobile Optimization.
4. SEO basic rule: optimize loading times
How important is the loading time for your search engine optimization? Pagespeed has been an official SEO ranking factor since July 9, 2018. In my opinion, however, the drop in user data that a page receives when the loading time is reduced or worsens is much more critical.
Let’s get to the point: What is more annoying than a lame website? For me, the effect on search engine optimization is somewhat secondary.
There are numerous tools with which the Pagespeed can be measured and analyzed—starting with Google Analytics, through Google PageSpeed Insights to many other tools like Pingdom or GTmetrix.
My recommendation is always to start with a free tool from Google. Pagespeed Insights is now using the data from Google Lighthouse and has improved significantly. And my credo is that if you primarily optimize for Google search (i.e., SEO (Search Engine Optimization)…), then at least the Google tools (even if they are not the best on the market) should not do anything have complained.
Pagespeed Insights divides its assessment into many areas such as the mobile Pagespeed or on the desktop. Otherwise, I find the value “time to interactivity” the most important because if the rest of the page is still loading, I’m only interested in the second place.
Apart from the fact that Pagespeed is a ranking factor and therefore very important for the algorithm, there are also many other reasons for optimizing the loading time on a website:
1. Crawling the website:
With the loading speed, you determine how often your site is crawled and how frequently the Google index updates your content. Since Google bot only has a specific budget, slow-loading websites are not crawled as quickly and intensively as other websites.
2. Sales:
There are some myths or theories as to how much revenue is lost in the online shop with reduced loading time. Some speak of 5% per second, which loads the page longer. Others mention other values that certainly also vary depending on the industry or are also heavily dependent on the competition.
The fact is: A slow loading time jeopardizes the SEO rankings and thus the sales or the whole search engine marketing strategy unnecessarily.
3. The user data:
Here too, the different data exist in the network. A customer will surely wait longer if he can only buy a particular product there on this one website (e.g., from a monopolist). If there are many other websites on which the same product can be obtained, the bounce rates are certainly significantly higher.
If the bounce rate is too intense and the page’s length of stay is too short, this can be seen in the lost (or not won) rankings. In other words, the SEO data will deteriorate significantly.
5. SEO basic rule: Provide content with added value
Since Google is still primarily a text-based search engine, the text remains highly relevant to the success of your search engine optimization (Search Engine Optimization).
Easy to say but challenging to implement. The main question that you have to ask yourself again and again when producing content: Does the generated content offer real added value?
If you can’t answer yes to this question, you can save yourself time too!
Think carefully about what information needs your users or potential customers have and try to satisfy them. This can be content that is closely related to the conversion (e.g., product tests) or material that fits in with a topic (e.g., the issue of health if I want to sell running shoes!).
The content is not about placing your product or company in the center, but about creating content that makes you appear as an expert or the best point of contact for the topic.
Typical content with added value is e-books, white papers, webinars, checklists, or studies. Of course, magazine articles are also included, insofar as they have been written with particular professional depth.
6. SEO basic rule: optimize the heading structure
The heading structure is the semantic backbone of your web or subpage!
Especially in times of absolute content overload, the headline structure is becoming increasingly important to give the reader a quick overview of what the article is all about. The headings are often the basis for the summary of a text, which also helps to a) get a better overview and b) use jump labels to navigate the reader to the relevant text.
A clear headline structure can be seen here. You are ascending, from h1 to h2 and h3. h3 elements are subtopics, again of h2 headings. The heading structure is highly relevant for your search engine optimization.
The logical order is interrupted here.
The user of your website must capture the content quickly and efficiently so that the probability of a jump is reduced mainly if you write about a topic that many others have already buttoned up in front of you.
The heading structure is also essential for the search engines because you significantly simplify the work of the web crawlers and so they can capture your page faster.
The following headings exist and are relevant for search engine optimization:
h1: There can be a maximum of one h1 per subpage. The h1 is very SEO-relevant and should always carry your most important keyword for the bottom. Usually, the h1 should also be the headlines of the respective document and also has the task of attracting your readers’ attention and thus ensuring a higher CTR from Google on your website.
h2: The h2 headings offer an excellent opportunity to use so-called semantically relevant keywords (for the main keyword) or related key terms. Also, the h2 lines should divide the article into its main areas.
A little tip: The h2 is the right place for questions and can be labeled as a Google Answer Box using the structured data.
h3: In the order of the heading structure, these headings are reserved for the less important topics. But what already applies to h2 also applies to h3. The perfect place to place other semantically matching keywords.
Checklist for your heading structure:
- Does your subpage have exactly one h1 heading?
- Is this h1 heading unique and stimulates to click?
- Is the main keyword of this subpage integrated?
- Are semantically matching keywords integrated into the h2 and h3?
7. SEO basic rule: earn links honestly
Last but not least, in addition to the technical and content-related aspects, the area of link building (off-page Optimization) is also part of proper search engine optimization (search engine optimization).
In very competitive industries, in particular, useful links are required to place in the Top10.
But be careful: no other area is as controversial as link building. While some search engine optimizers deliberately stay away from the whole off-page work, others swear by the effects.
No area provides more punishment potential on the part of Google and is so difficult to see through.
My tip at the point is, don’t pay money for backlinks, but invest your money in the right strategies on how to get good backlinks (recommendations) from topic-related websites through entire content or unique campaigns.
Remember: buying a link is not only legally questionable but is also clearly against Google guidelines and thus offers a constant target for potential penalties.
But if you think deeply into the whole of page topic, you will surely come up with one or the other innovative idea of how you can have your website linked.
